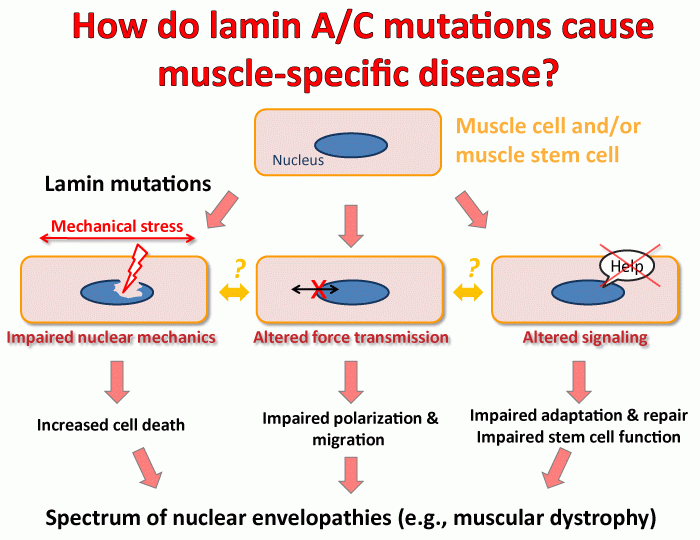
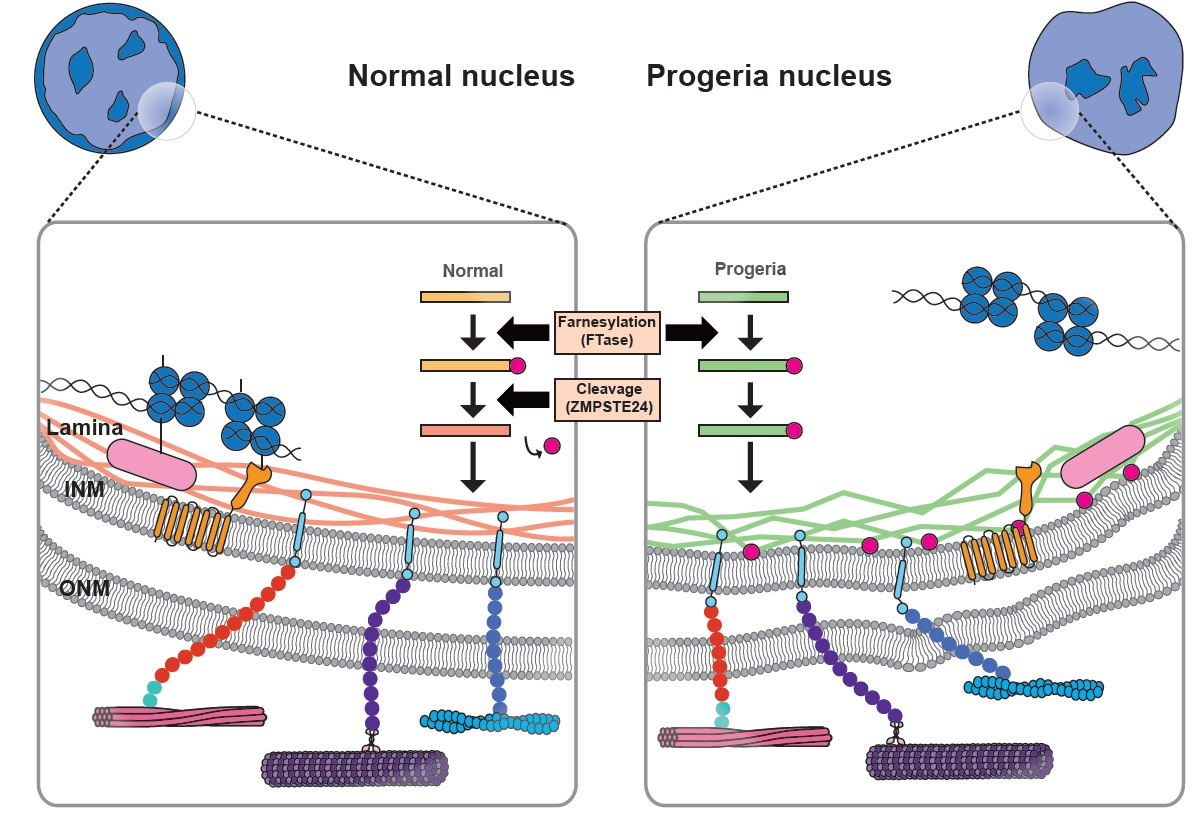
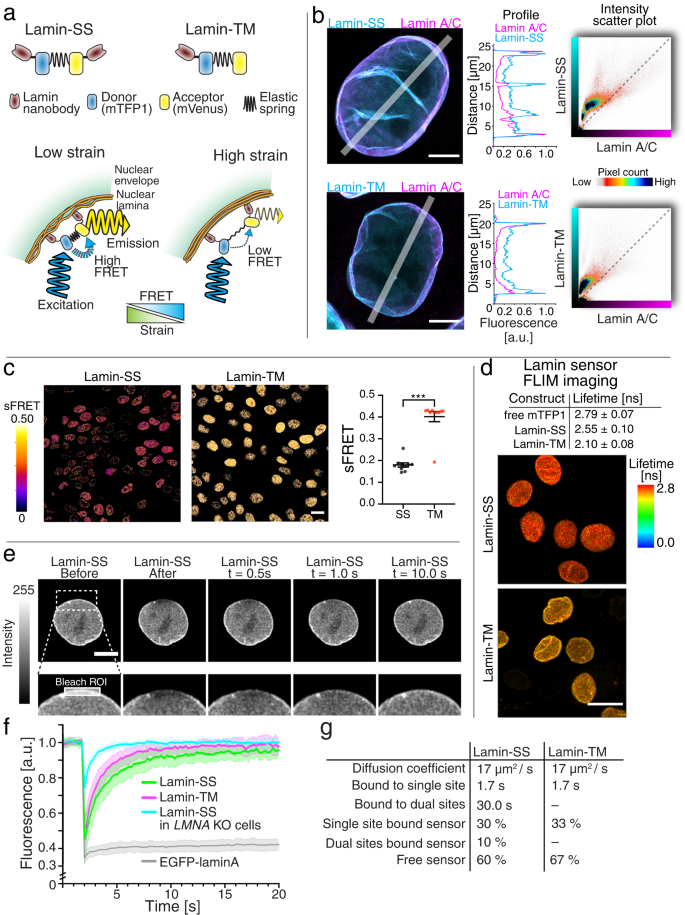
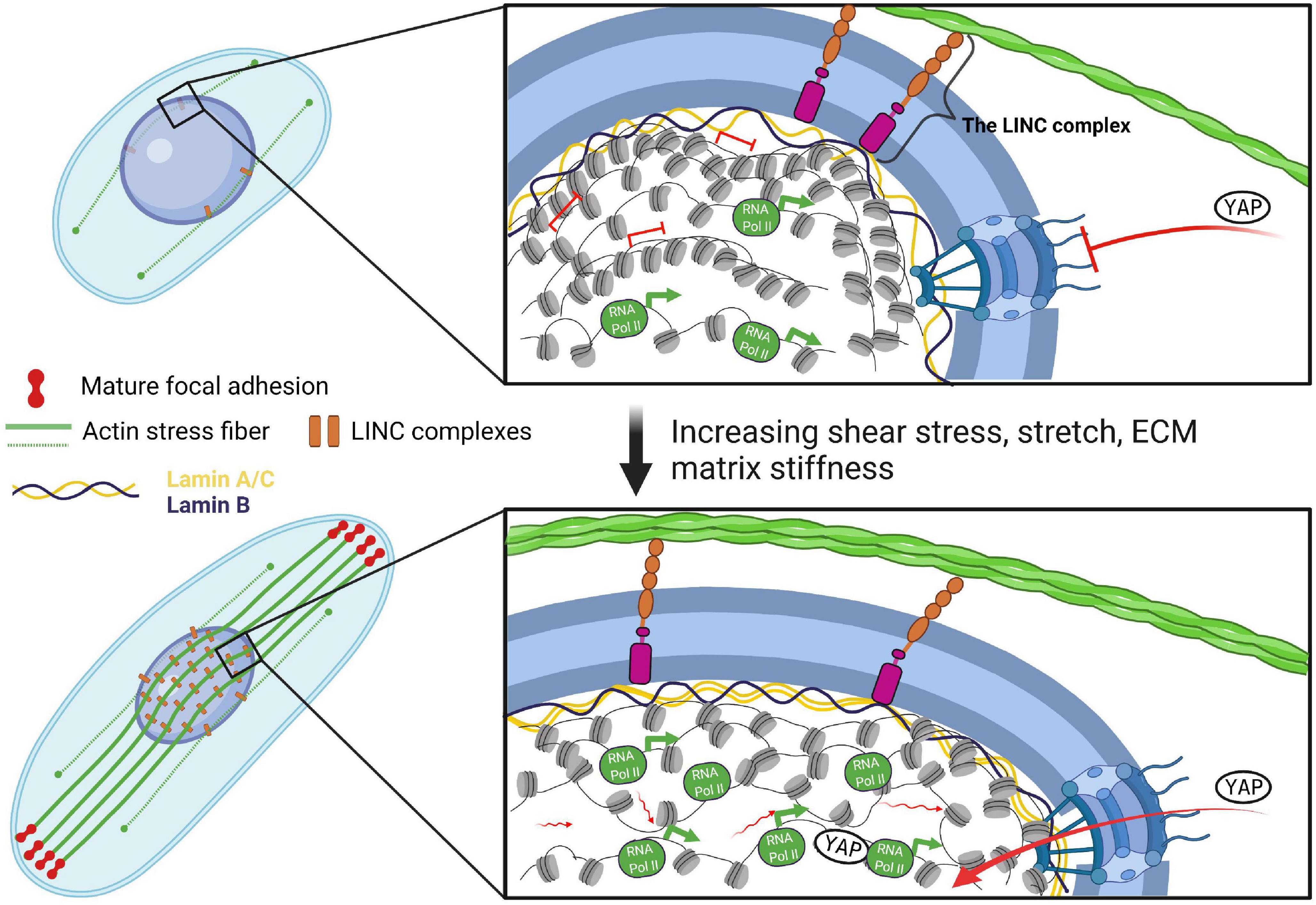
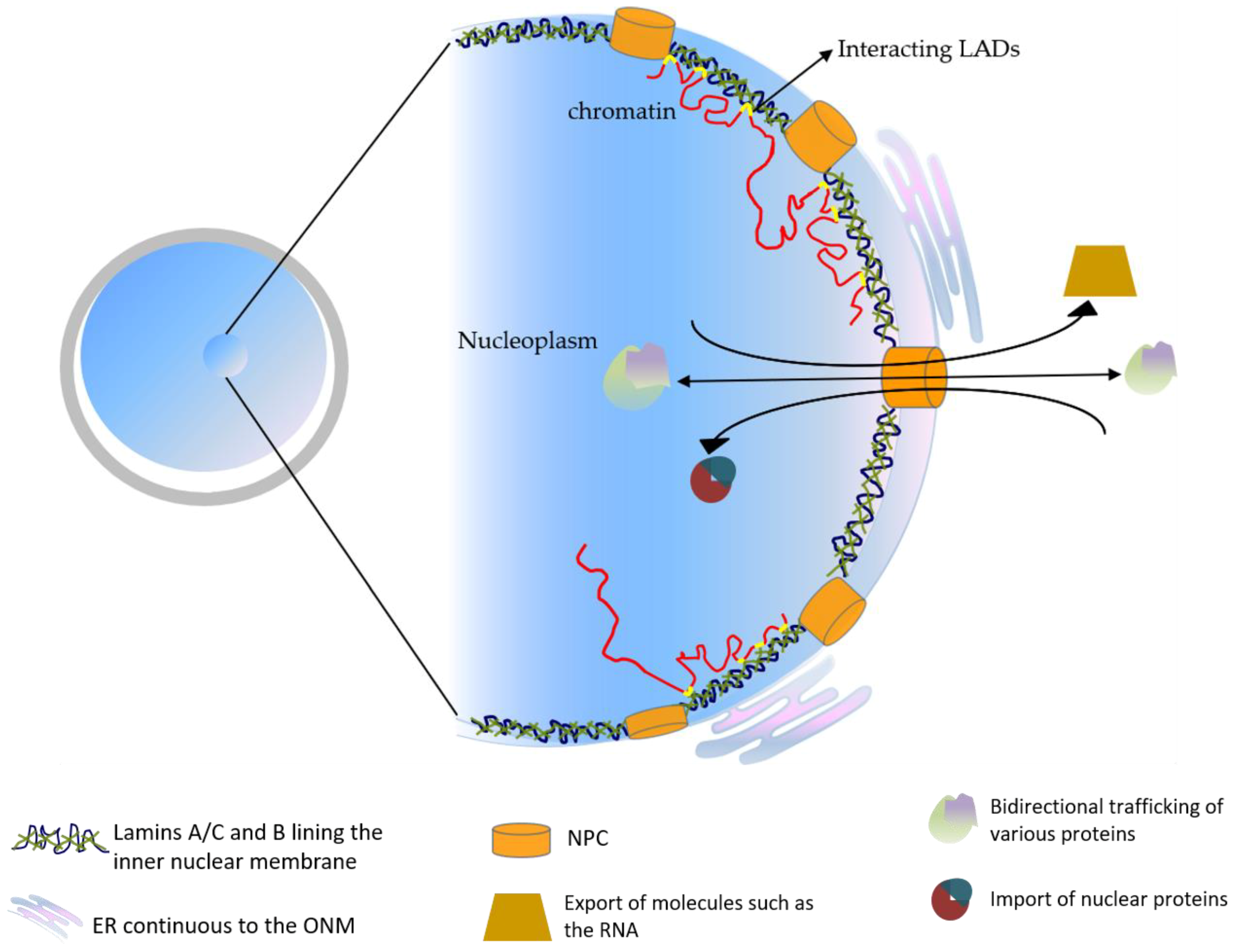
Nuclear lamin isoforms differentially contribute to LINC complex-dependent nucleocytoskeletal coupling and whole-cell mechanics | PNAS
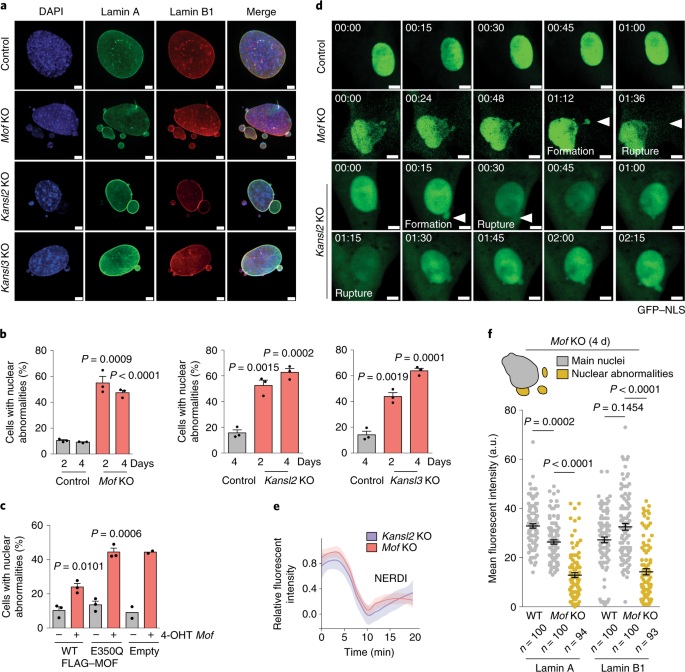
The NSL complex maintains nuclear architecture stability via lamin A/C acetylation | Nature Cell Biology
Molecular assembly of nuclear lamina and structure of a lamin filament.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Nuclear Envelope Lamin-A Couples Actin Dynamics with Immunological Synapse Architecture and T Cell Activation | Science Signaling

Proteins as mechanomarkers. Expression of Lamin A, YAP and MRTF-A are... | Download Scientific Diagram
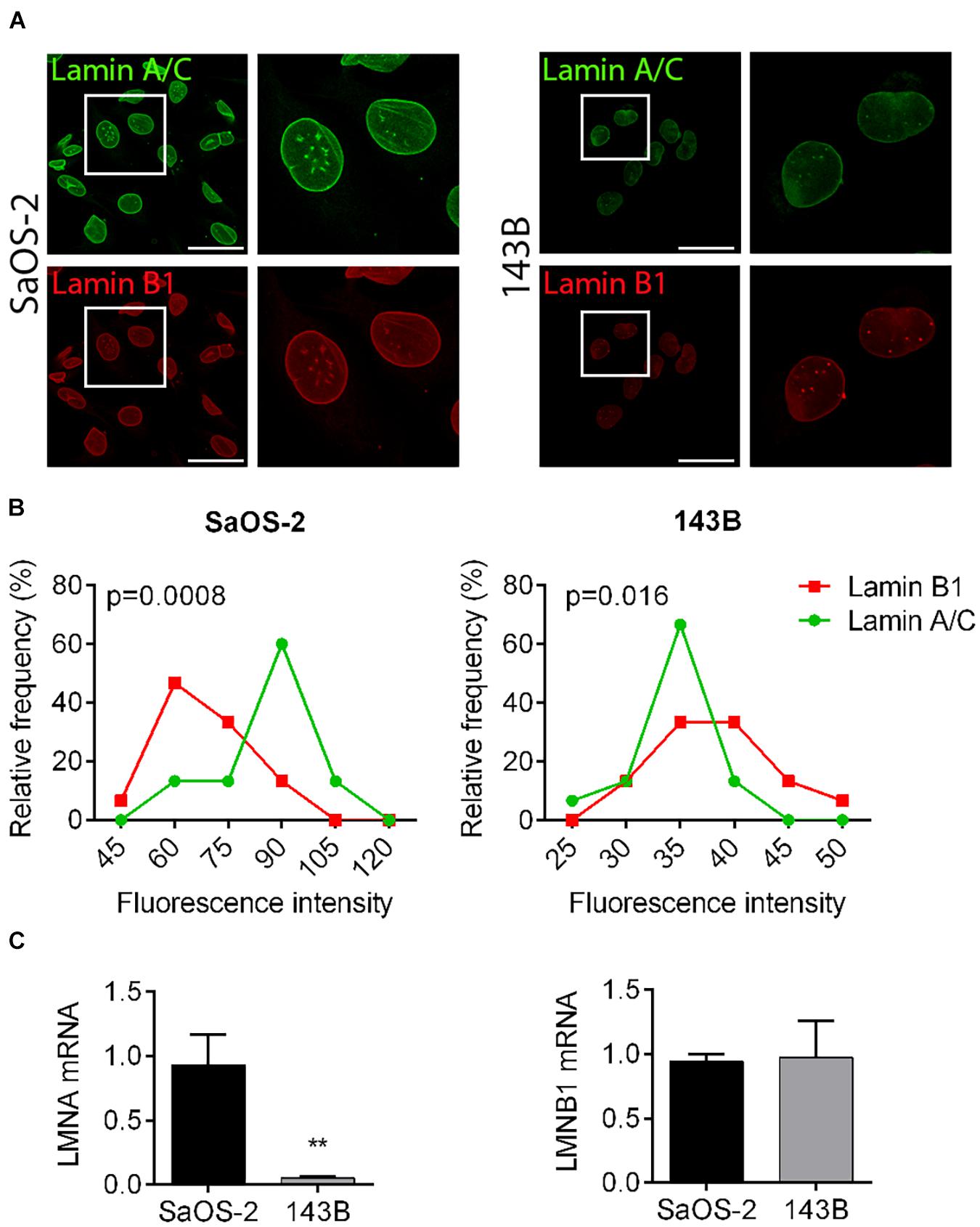
Frontiers | Lamin A/C Mechanosensor Drives Tumor Cell Aggressiveness and Adhesion on Substrates With Tissue-Specific Elasticity
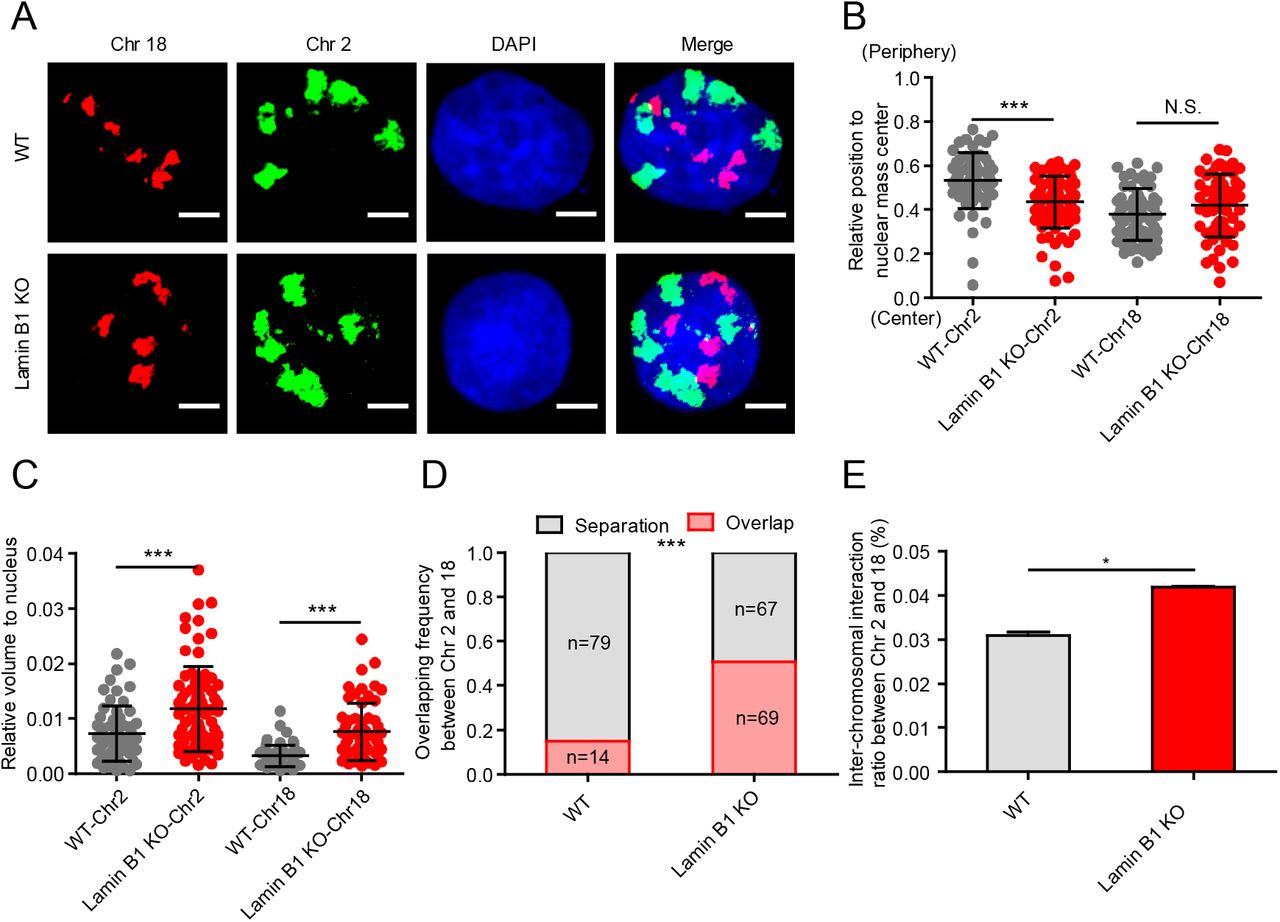
Chromatin-lamin B1 interaction promotes genomic compartmentalization and constrains chromatin dynamics | bioRxiv
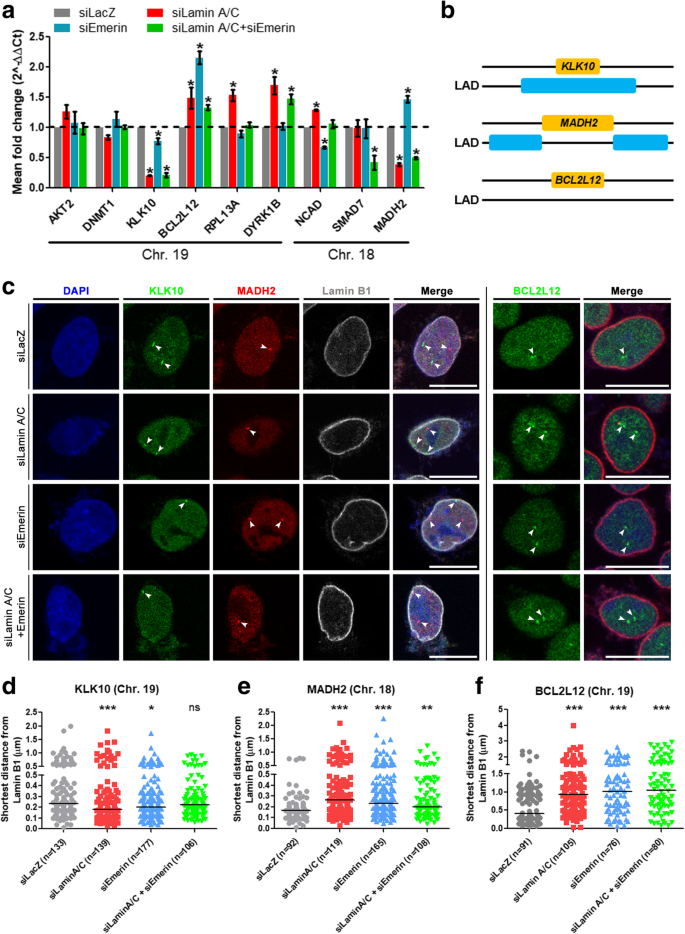
Lamin A/C and Emerin depletion impacts chromatin organization and dynamics in the interphase nucleus | BMC Molecular and Cell Biology | Full Text

Schematic model of the interplay between nuclear envelope proteins and... | Download Scientific Diagram

Linker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton Complex Proteins in Cardiac Structure, Function, and Disease | Circulation Research